You have probably noticed that the healthcare industry is generally far away from being “tech-ed” and armed to the teeth with tech innovations. HIMSS Healthcare Survey (held in 2021) pointed out that 73% of healthcare providers still use outdated legacy systems. What can we talk about if 20% still run Windows XP?
Doctors struggle to access patient records, nurses waste time navigating labyrinthine systems, and appointments get rescheduled due to software malfunctions. If there is software to arrange appointments at all. As you already understand, this is a harsh reality for many healthcare providers grappling with the consequences of digital debt.
Tech debt, in the healthcare context, refers to the accumulation of outdated technology, poorly written code, and unaddressed technical issues. Think of it like a credit card bill for past technological choices. Every quick fix, every workaround, every postponed upgrade adds to the debt, accruing interest in the form of inefficiencies, security vulnerabilities, and, ultimately, compromised patient care.
Banner Health — an excellent example. A large healthcare system in the US in 2016 experienced a data breach stemming from unpatched vulnerabilities in their outdated software, exposing the personal information of about 3M patients. The matter of cost was about USD 88 million settlement, not to mention the reputational damage and patient trust eroded.
Tech debt remediation in healthcare is not merely a matter of operational efficiency; it’s all about strategy. The stakes are high, with patient outcomes and institutional reputation hanging in the balance. Much like a well-maintained medical facility fosters trust and reliability, a healthcare organization's IT systems, devoid of technical debt, ensure uninterrupted access to critical patient information, streamline workflows, and ultimately enhance the quality of care.
Empower your IT team to focus on innovation and growth by outsourcing your technical debt management
Understanding Healthcare Tech Debt
The healthcare industry swims in a sea of data, with patient records, diagnostic images, and treatment plans constantly churned and accessed. Yet, beneath this surface, an insidious enemy lurks healthcare tech debt. Technical debt in healthcare represents the cost of quick fixes, shortcuts, and outdated systems that accumulate over time, threatening to capsize even the most well-intentioned healthcare organization. And there is no way legacy healthcare services reviews will help since the overloaded systems can lead to data leaks.
Types of Tech Debt in Healthcare
Often, when a healthcare company encounters technical debt, it comes in different types with its “partners in crime” — various bugs. They accumulate and down the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare operations. If your company pretends to become a healthcare leader, you should recognize and address at least these three types.
1/ Legacy Systems
In healthcare, legacy systems stand as pillars of the past, often housing critical patient information. These outdated systems become a type of technical debt as they hinder the integration of modern technologies, slowing down processes and impeding interoperability.
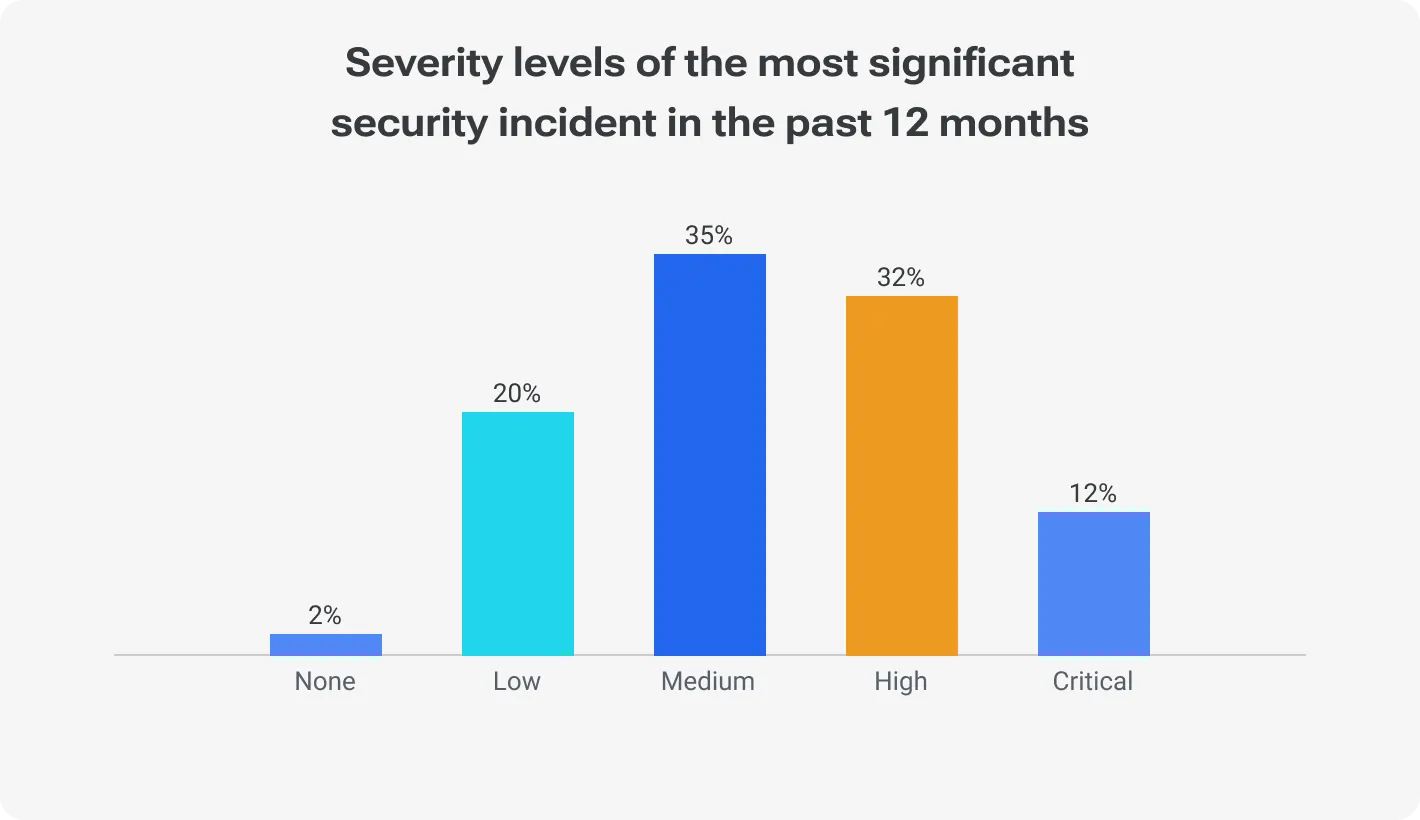
A staggering 79% of healthcare companies had security accidents of medium and higher levels.
However, archaic software applications continue to haunt many healthcare providers. These often homegrown or cobbled-together systems lack scalability, interoperability, and security features critical for modern healthcare needs. Remember the Millennium Bug scare of 2000, largely caused by outdated COBOL code still powering critical infrastructure? Healthcare remains vulnerable to similar disruptions due to its reliance on legacy systems.
2/ Outdated Infrastructure
The backbone of any healthcare institution lies in its infrastructure. Outdated servers, network systems, or hardware can create bottlenecks, jeopardizing the efficiency of medical operations and impinging on the timely delivery of care.
Just as a hospital with flickering lights and unreliable plumbing hinders care delivery, outdated IT infrastructure creates bottlenecks and vulnerabilities. The most clear-cut example is aging servers struggling to handle the ever-growing volume of electronic health records (EHRs) and medical images. As far as 2023, a ransomware attack on at least 30 US healthcare services crippled operations for days due to vulnerabilities in their outdated infrastructure, impacting patient care and costing millions in recovery efforts.
3/ Inadequate Security Measures
With the constant threat of cyberattacks, healthcare organizations must fortify their digital defenses. Just because healthcare organizations with porous security postures become prime targets. Unpatched vulnerabilities in outdated software, weak access controls, and lack of employee cybersecurity awareness create gaping holes in data defenses.
The 2021 HIMSS Cybersecurity Survey revealed that 45% of healthcare organizations lacked a formal cybersecurity incident response plan. Well, that’s a perfect opportunity for intruders to bring about data breaches and financial losses.
Why tech debt roadmaps don’t work
Impact of Tech Debt on Healthcare Operations
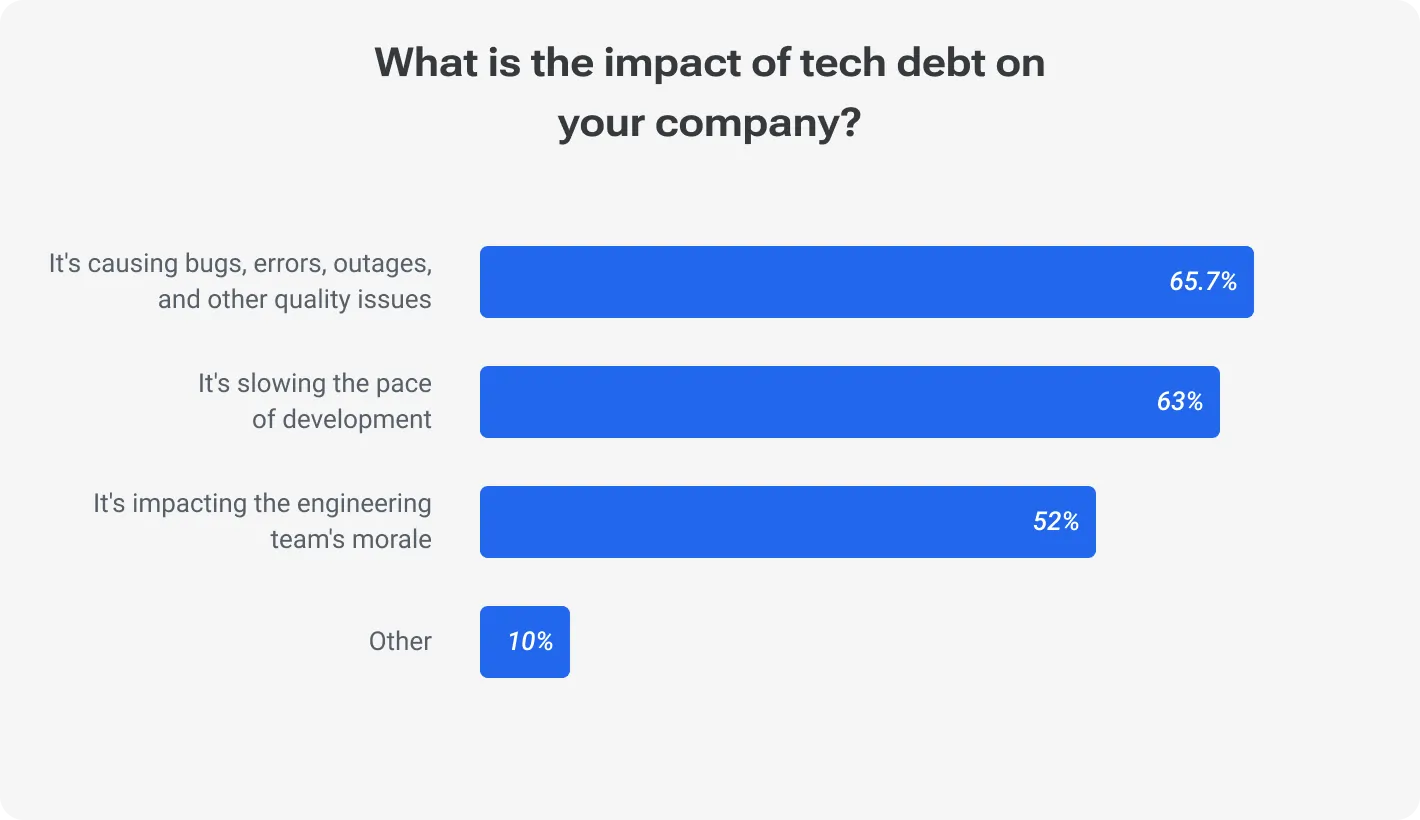
The ramifications of technical debt extend beyond mere inconvenience; they strike at the core of operational efficiency, patient safety, and regulatory compliance. By the way, the consequences of unaddressed tech debt extend far beyond IT challenges. Here's a closer look at some key areas.
Decreased Efficiency
Almost always, tech debt gets expressed in slower workflows and fragmented processes. Outdated systems struggle to keep pace with the demands of modern healthcare.
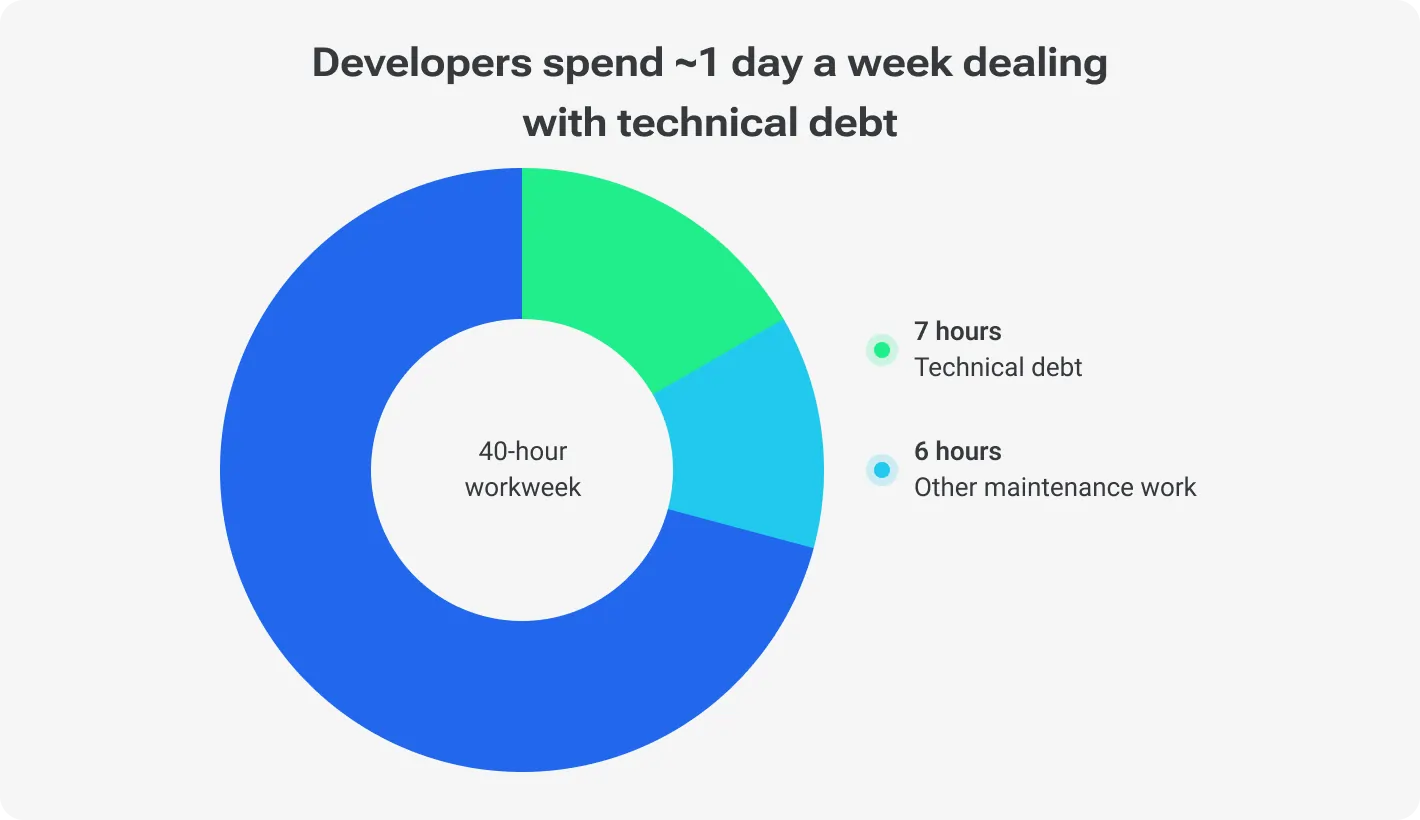
Imagine nurses spending hours hunting for patient records buried in inherited systems or doctors battling unmanageable interfaces to input data. Tech debt translates to wasted time, frustrated staff, and, ultimately, reduced patient throughput and productivity. A 2023 study by KLAS Research found that outdated technology costs US hospitals an average of USD 52,000 per physician per year in lost productivity.
Other studies show that healthcare institutions grappling with legacy systems experience a 20% decrease in operational efficiency over a five-year period.
Increased Risk of Errors
Healthcare is an industry where precision is paramount. And technical debt introduces an elevated risk of errors. Outdated software and inadequate testing protocols create an environment where medical professionals may encounter glitches.
Inaccurate medication dosages, delayed diagnoses, and communication breakdowns are just some of the potential consequences of tech debt-induced inefficiencies. All that stuff introduces errors into critical workflows, impacting patient safety and potentially leading to costly medical malpractice lawsuits. Pascale Carayon, PhD and Professor, conducted research in 2021 and found that EHR-related errors contribute to nearly 1,600 patient deaths annually in the US alone.
Compliance and Regulatory Challenges
Healthcare operates within a stringent framework of regulations and compliance standards. Technical debt, particularly in terms of outdated security measures and legacy systems, poses a challenge to meeting these standards. This exposes institutions to regulatory penalties and legal repercussions.
A 2021 report by the Office for Civil Rights (OCR) revealed that healthcare entities accounted for the highest number of HIPAA violations (34,077), with many stemming from inadequate data security measures.
Another study by the University of North Georgia indicates that 80% of healthcare organizations struggle to maintain compliance in the face of evolving regulatory requirements, primarily due to technical debt.
Signs of Tech Debt in Healthcare
Undercurrents of tech debt can manifest in various signs, often unnoticed until they crystallize into operational challenges. Recognizing the early warning signs is crucial for taking proactive steps to avoid costly disruptions. Not everyone can spot tech debt at the early stage, this is a priceless tech skill. So, below, we listed five key indicators that will help you to develop this flair on tech debt burden.
1. Slow System Performance
The latency in system response times is a telltale sign of potential tech debt. Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) related to system response. Users experience long loading times, unresponsive interfaces, and frequent application crashes. A significant deviation from baseline metrics may indicate underlying inefficiencies. Look for metrics like increased response times, page load times exceeding industry benchmarks (e.g., >3 seconds), or user complaints about system delays.
2. Difficulty in Integrating New Technologies
Almost any business must be flexible and adaptable. Otherwise, it’s doomed. For this point, the struggle to seamlessly integrate new technologies points to existing tech debt. Data silos emerge, APIs refuse to cooperate, and customization requirements skyrocket. Keep a keen eye on the interoperability of existing systems with emerging technologies. Frequent roadblocks, compatibility issues, and prolonged integration timelines are red flags.
3. Rising Maintenance Costs
Avoiding technical jargon overload, let’s say that when maintenance costs constantly escalate, probably, this is due to accumulating technical debt. Patching bugs, fixing workarounds, and maintaining outdated infrastructure consumes IT resources and diverts budgets away from strategic initiatives. Track the cost of routine maintenance tasks, including bug fixes and system updates. A notable increase in these expenditures may indicate underlying inefficiencies demanding attention.
4. Increased Frequency of System Failures
Frequent system failures are clear indicators of technical debt. Monitor incident reports, system logs, and error rates. A spike in the frequency of system failures is a warning signal under any circumstances, but even more so when it is an unexpected downtime. This may suggest deeper issues in the software architecture.
But don't just track the number of system failures; delve deeper into the nuances to understand the true extent of your tech debt burden.
Analyze the nature of failures: Are they random glitches or recurring issues tied to specific functionalities or modules? Recurring failures point to deeper architectural problems within your legacy systems.
Measure downtime impact: There the most important impulse to look out for is the duration of outages and their effect on critical operations. A seemingly minor system crash affecting appointment scheduling for hours can have significant downstream consequences.
Monitor near misses: Track and analyze "near misses" where systems almost crashed or exhibited instability. Of course, not all errors result in complete system failures; however, they’re also worth noticing as they indicate potential vulnerabilities waiting to explode.
For example, a hospital experiences frequent EHR outages. This causes delays in patient care and administrative disruptions. Obviously, they need a closer analysis. This way, they can discover the root cause lies in outdated database servers struggling to handle the growing volume of electronic records. This signals a need for infrastructure upgrades to prevent future critical failures.
5. User and Patient Dissatisfaction
User experience is king, hands down. A decline in users’ satisfaction can be attributed to tech debt affecting the experience. Make it a habit to survey your patients regularly and see if everything is okay. Consistent negative sentiments and declining satisfaction must tip you of accumulating technical debt.
There is a thing. Listen closely to the voices of your staff, too, as their frustrations also often reveal hidden pockets of tech debt.
Analyze user feedback: Look for recurring themes in staff surveys, service desk tickets, and user forums. Do clinicians consistently complain about specific functionalities within an EHR system? Are patients frustrated with long wait times due to slow appointment scheduling software?
Track sentiment analysis: Leverage social media monitoring tools and patient satisfaction surveys to identify negative sentiment related to technology experiences. A spike in complaints about data privacy concerns might indicate inadequate security measures, a form of tech debt.
Conduct focus groups: Engage directly with users and patients through facilitated discussions to understand their pain points and technology-related challenges. Hearing their firsthand experiences can illuminate areas where tech debt creates friction and hinders service delivery.
When you are aware of an existing problem, take action! Pro-acti-ve-ly. Identifying and addressing tech debt at its nascent stage ensures a resilient and responsive healthcare IT ecosystem. By the way, 15% of those surveyed in 2021 developers were sure that a structured system for tackling code debt would boost their productivity by 2x times.
Strategies for Spotting Tech Debt
Tech debt can pop up invisibly within your IT infrastructure, waiting to cause disruptions and drain resources. Yet, proactive companies can employ various strategies to nip it in the bud before it snowballs into bigger problems. Here are effective approaches to proactively spot code debt before it evolves into operational challenges.
1/ Regular Technology Audits
Don't wait for problems to swallow you; you should be proactive — schedule regular technology audits to assess your IT infrastructure. A comprehensive audit examines code quality, system architecture, and adherence to coding standards.
These comprehensive evaluations, conducted by internal or external experts, can identify outdated systems, security vulnerabilities, and code quality issues that contribute to tech debt.
Gartner revealed that organizations conducting regular IT audits experience about 20% fewer system outages. We suppose Gartner is worth trusting. A remarkable example comes from the tech giant IBM, where routine audits played a pivotal role in identifying and rectifying tech debt issues, resulting in improved system reliability.
2/ Monitoring System Performance Metrics
Robust monitoring systems are great aiders in tracking key performance metrics continuously. Deviations in response times, server loads, and error rates can serve as early warning signs. Very interesting stats were published by the Journal of Healthcare Information Management on Tanzania's healthcare market. Companies that actively monitor system performance reduce unexpected downtime by 20%.
In other words, deviations from established baselines and industry benchmarks can signal potential issues beneath the surface. For example, a healthcare organization monitoring EHR access times discovers consistently slow loading speeds exceeding industry averages. This prompts further investigation, revealing inefficient database queries and outdated server hardware, both contributing to tech debt.
3/ Keeping Abreast of Industry Standards and Best Practices
The technology landscape is constantly evolving, and so are best practices for managing IT infrastructure. Regularly benchmark your systems against industry standards and best practices because a stitch in time saves nine. Keeping up with evolving benchmarks doesn’t ensure your healthcare technology aligns with the latest advancements. However, staying informed about industry standards and security protocols allows you to compare your current state to optimal benchmarks and identify areas where your systems might be falling behind. A notable case — the Mayo Clinic, which attributed a 30% improvement in patient care efficiency to aligning their systems with emerging industry standards.
Additionally, a 2023 study by IDC found that companies adhering to industry best practices for data security achieve significant reductions in cyberattacks and about 60% lower data breach costs.
4/ Machine Learning and AI-powered Tools
As technology advancements accelerate, so do the capabilities of detection tools. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of system data to identify patterns indicative of tech debt, such as code anomalies, security vulnerabilities, and performance bottlenecks. Imagine a hospital utilizing an AI-powered solution to analyze EHR usage patterns and discover redundant data entries and inconsistencies. Not bad, right? This move uncovers hidden debt within their data management practices.
5/ Collaboration and Cross-Departmental Communication
Encourage collaboration and open communication between IT, clinical, and administrative departments. Cross-functional dialogue helps identify operational pain points caused by tech debt. A study published in the Journal of Health Management and Informatics found that organizations with strong cross-departmental communication experience a reduction in implementation delays due to tech debt-related challenges.
Mitigating and Avoiding Tech Debt
The most interesting thing is that unveiling your tech debt is just only half the battle. The true victory lies in crafting a strategic plan for mitigation and avoidance (and actually following this plan). But what does stop you from considering tech debt remediation as an opportunity to optimize your IT landscape and drive innovation in healthcare delivery? Let's explore concrete steps that empower healthcare leaders to fortify their digital infrastructure for sustained excellence.
1/ Prioritizing Technology Upgrades
Not all upgrades are equal. Resist the urge to overhaul the whole shebang at once. Rushed upgrades can introduce their own set of challenges, potentially exacerbating code debt. Prioritize critical systems experiencing frequent failures, security vulnerabilities, or hindering user productivity. A case in point is the National Health Service’s attempt to upgrade its IT infrastructure, which faced implementation challenges and resulted in unplanned downtime. This is not to mention user disruptions.
Nuance to look out for: Don't be seduced by the latest bells and whistles. Prioritize based on impact, not hype. Focus on mission-critical systems experiencing:
Frequent failures: Banal a bit, but still vital. Identify systems causing operational disruptions and impacting patient care directly.
Security vulnerabilities: Patch outdated systems harboring known exploits before attackers discover them.
User productivity bottlenecks: Address systems creating inefficiencies and frustration for clinicians and staff.
Pitfall: Avoid the "rip and replace" mentality. Conduct thorough cost-benefit analyses considering: integration complexity (that ensures compatibility with existing infrastructure), training costs, and sunset costs (understand vendor support lifecycles and avoid stranded assets).
2/ Investing in Scalable and Interoperable Solutions
Embrace technology built for growth and collaboration. Opt for solutions with open APIs and standardized data formats to facilitate seamless integration with existing systems and future innovations. However, the selection of such solutions requires careful consideration. In healthcare, interoperability challenges can arise when integrating diverse systems. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services' push for interoperability faced hurdles due to variations in data standards. To mitigate risks, healthcare organizations must rigorously assess the scalability and interoperability of solutions, ensuring seamless integration without compromising efficiency.
Nuance to look out for: Embrace open standards and APIs and avoid vendor lock-in. Scrutinize the following:
FHIR compliance: Enables seamless data exchange with other healthcare systems.
Cloud-based solutions: Offer inherent scalability and easier integration with future innovations.
Modular architecture: Allows you to add or remove functionalities as your needs evolve.
Pitfall: Avoid overly complex solutions with excessive customization requirements. Take into account user adoption (simple is better), integration challenges (don’t forget about compatibility in this case, too), and vendor dependence.
3/ Implementing Robust Security Measures
Proactive security is an investment in patient trust, operational resilience, and financial stability. Regularly patch vulnerabilities, conduct penetration testing, and prioritize ongoing security awareness training for staff. However, the pitfall lies in assuming a one-size-fits-all approach. Overly stringent security measures may impede workflow efficiency.
Nuance to look out for: Go beyond basic antivirus and firewalls. Implement a layered security approach. This is not as easy as pie, but there is a hint of what your layers may include:
Data encryption at rest and in transit: Safeguard sensitive patient information wherever it resides.
Multi-factor authentication: Add an extra layer of protection beyond passwords.
Endpoint security: Secure all devices accessing your network, including personal devices.
Regular penetration testing: Identify and address vulnerabilities before attackers do.
Pitfall: Try to balance security with usability because no one wants to lose their bearings in complex software. Ensure security measures don't create excessive friction for authorized users. Don’t forget to educate staff on cybersecurity best practices to avoid human error risks. Last but not least — have a clear plan for identifying, containing, and remediating security breaches.
4/ Collaboration between IT and Healthcare Professionals
There is usually an abyss between technical and non-technical people: in understanding the technical details, the health protection system of a particular country, and a gulf in communication in general. This needs to change. If you want to be a leader, establish adequate interaction between technical and non-technical staff. First, avoid technical jargon overload in documents and software interfaces. Translate tech speak into a language clinicians understand. Focus on the "why" behind technology solutions, not just the "how." A seamless collaborative environment ensures that technology solutions align with clinical workflows, mitigating the risk of introducing tech debt through miscommunication.
Nuance to look out for: Create a culture of open communication and shared goals. How to streamline communication? Use:
Joint workshops: Bring IT and clinical teams together to discuss pain points and potential solutions.
Clinical champions: Empower clinicians to advocate for technology adoption and provide user feedback.
Data visualization tools: Translate complex technical data into easily understandable formats for clinicians.
Pitfall: Avoid technical jargon and one-sided conversations. Explain technology in terms of its clinical benefits and impact on patient care. Their insights and workflow challenges may bring more value than you think. Recognize and reward successful collaborations that drive positive outcomes.
To sum it up
The meticulous navigation of digital debt emerges as a critical point. On average, every healthcare company has at least 20% to 40% of accumulated tech debt, leading to compromised patient care and operational inefficiencies.
But what’s crucial is that tech debt isn't just an IT concern. It’s pretty easy to hide and put the blame on technical people. That’s a huge mistake — the cost of internal miscommunication is simply too high.
Investing in robust security measures, scalable and interoperable solutions, and ongoing technology upgrades isn't just about solving immediate problems; it's about unlocking long-term benefits. Studies show that healthcare companies with proactive tech management experience 30% faster innovation cycles, 25% lower operational costs, and 40% fewer security breaches on average. These improvements inevitably lead to better patient outcomes, improved staff satisfaction, and a more sustainable future for healthcare delivery.
Gain an access to seasoned professionals specialized in managing technical debt